
And it runs in either modern 64-bit PC, old 32-bit machine, ARM64 OS like Phytium/Kunpeng, and mips64el Loongson 3A MIPS OS. The software now provides graphical user interface for Linux since version 1.0.52. Download them from the link below:ĭownload Ventoy a.) using Ventoy’s graphical app for Linux:
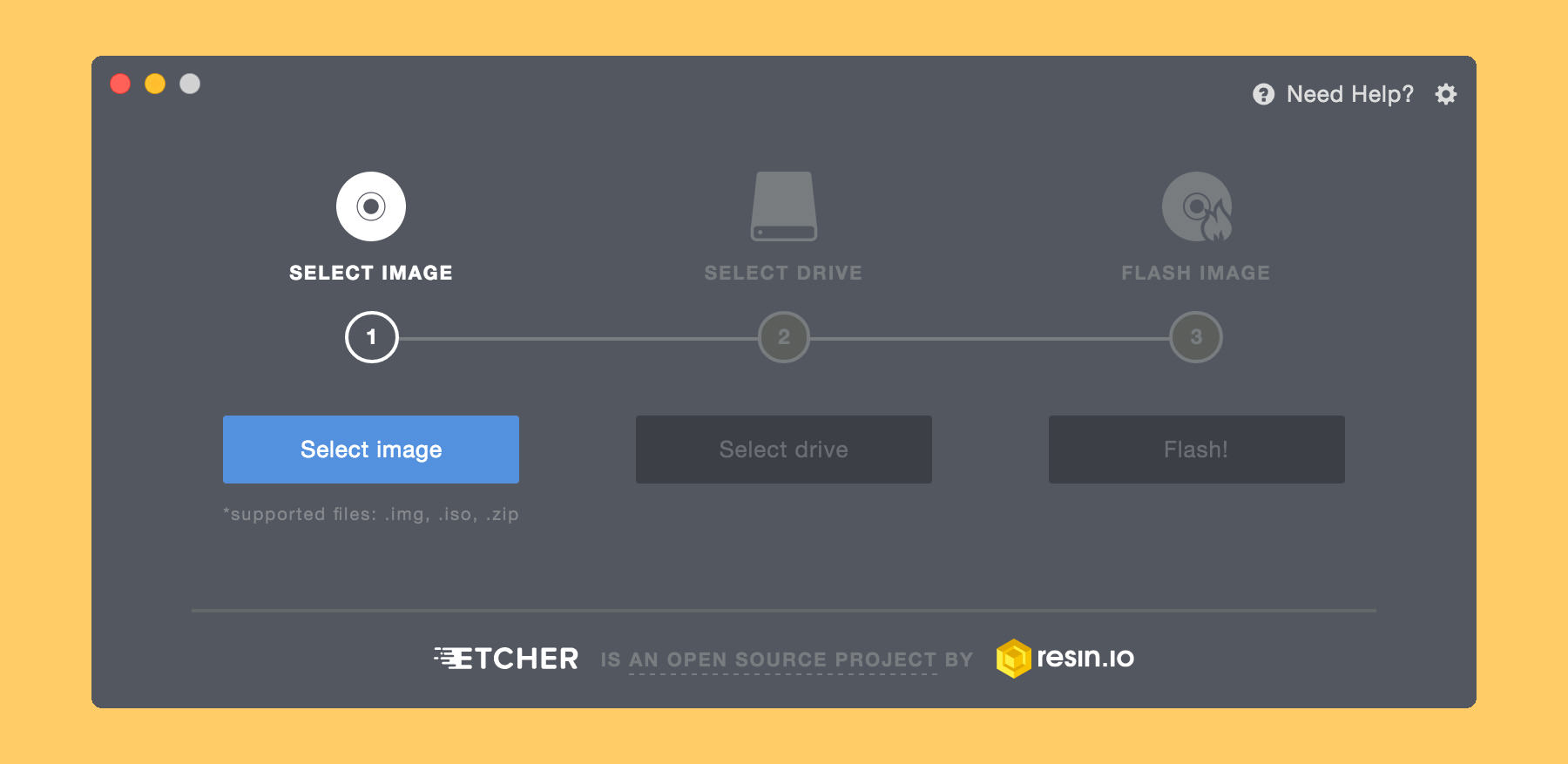
The software provides ISO image as well as installers for Windows and Linux.
Also support Local Disk, SSD, NVMe, SD Card. 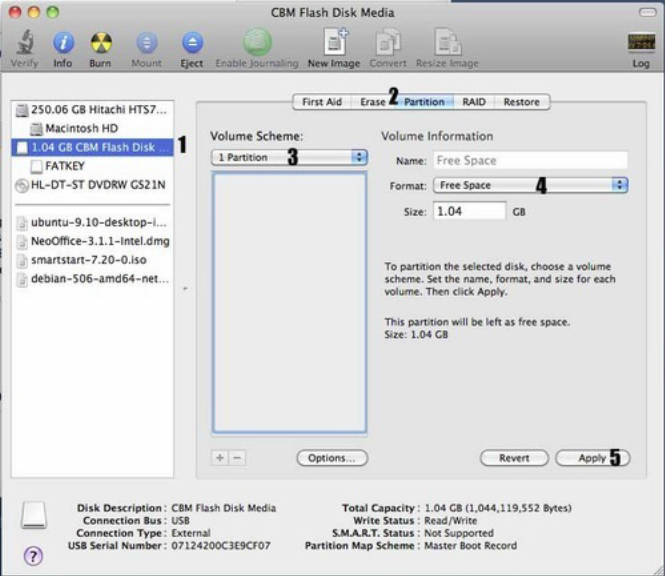 700+ ISO files supported (Windows, Linux, WinPE, Unix, Vmware, Xen). Save all other data along with ISO images, just like a normal USB driver. As many ISO images as your USB stick can store. Just copy ISO to USB and boot it! No extraction needed. Ventoy is a free and open-source tool written mainly in C. Ventoy will find what to boot and show them all in startup menu. Without extracting, just drag and drop to move ISO images into USB drive, and it will boot them! Like normal USB drive, you can put your photos and other data along with ISO images. With Ventoy, it just format your USB one time, create a small ( 34 MB in my case) EFI partition, and leave all other spaces free in another partition. Why Ventoy:ĭifferent to other USB creators, you don’t need to format your USB stick again and again to write data from ISO images. Now Ventoy is a good choice that I use often to try different operating systems. You can now quit Terminal and eject the volume.I used to create bootable Ubuntu USB installer with UNetbootin, then with Ubuntu’s built-in USB creator. When Terminal says that it's done, the volume will have the same name as the installer you downloaded, such as Install macOS Monterey. After the volume is erased, you may see an alert that Terminal would like to access files on a removable volume. Terminal shows the progress as the volume is erased. When prompted, type Y to confirm that you want to erase the volume, then press Return. Terminal doesn't show any characters as you type. When prompted, type your administrator password.
700+ ISO files supported (Windows, Linux, WinPE, Unix, Vmware, Xen). Save all other data along with ISO images, just like a normal USB driver. As many ISO images as your USB stick can store. Just copy ISO to USB and boot it! No extraction needed. Ventoy is a free and open-source tool written mainly in C. Ventoy will find what to boot and show them all in startup menu. Without extracting, just drag and drop to move ISO images into USB drive, and it will boot them! Like normal USB drive, you can put your photos and other data along with ISO images. With Ventoy, it just format your USB one time, create a small ( 34 MB in my case) EFI partition, and leave all other spaces free in another partition. Why Ventoy:ĭifferent to other USB creators, you don’t need to format your USB stick again and again to write data from ISO images. Now Ventoy is a good choice that I use often to try different operating systems. You can now quit Terminal and eject the volume.I used to create bootable Ubuntu USB installer with UNetbootin, then with Ubuntu’s built-in USB creator. When Terminal says that it's done, the volume will have the same name as the installer you downloaded, such as Install macOS Monterey. After the volume is erased, you may see an alert that Terminal would like to access files on a removable volume. Terminal shows the progress as the volume is erased. When prompted, type Y to confirm that you want to erase the volume, then press Return. Terminal doesn't show any characters as you type. When prompted, type your administrator password. 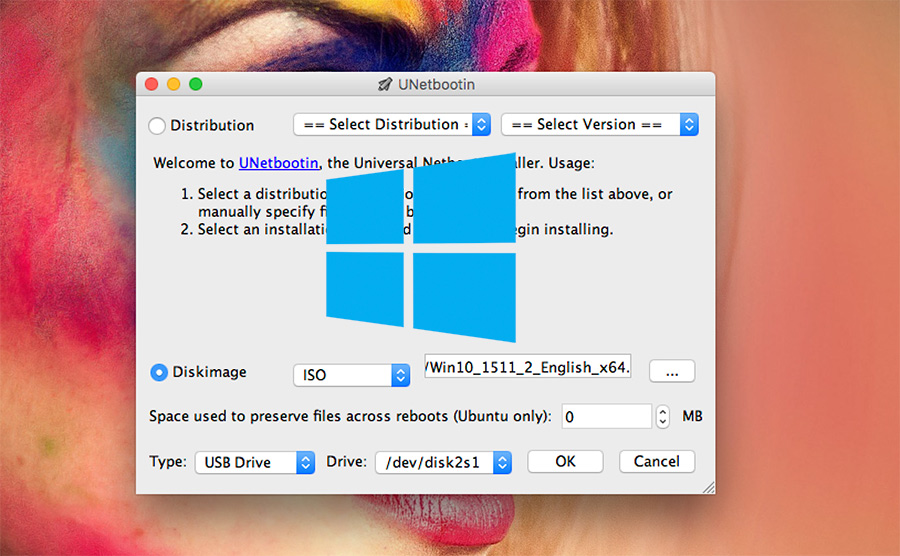
If the volume has a different name, replace MyVolume in the command with the name of your volume. Each command assumes that the installer is in your Applications folder, and MyVolume is the name of the USB flash drive or other volume you're using.

Type or paste one of the commands below into Terminal, then press Return to enter the command. Open Terminal, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. Plug in the USB flash drive or other volume that you're using for the bootable installer.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
